In the unique universe of financial exchanges, financial backers frequently look for new roads to differentiate their portfolios and amplify returns. Smallcase, a cutting-edge speculation instrument, has built up some decent forward momentum because of its innovative way of dealing with investing resources into the financial market. Understanding the significance of smallcase share prices and returns is fundamental for financial backers hoping to explore this rising speculation scene proficiently.
What are Smallcases?
Smallcases are expanded arrangements of stocks or trade exchanged reserves (ETFs) keenly weighted to mirror a thought, subject, or technique. These can go from areas like innovation, and medical care, or subjects like ESG (Ecological, Social, and Administration) to shrewd beta systems. Smallcases are organized by monetary specialists, information researchers, or examiners, offering financial backers a helpful method for putting resources into a particular topic or procedure with a single click.
Meaning of Smallcase Offer Cost
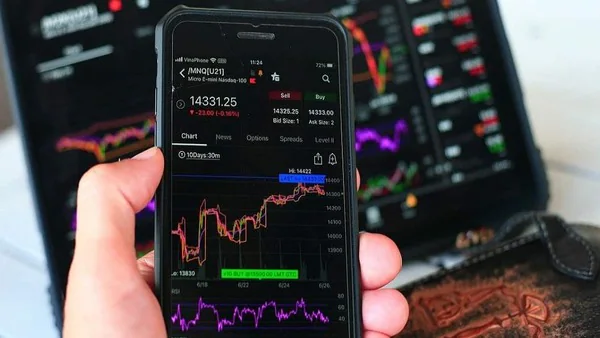
Smallcase share price mirrors the aggregate presentation of the fundamental stocks or ETFs inside the portfolio. The development of smallcase share prices is instrumental in deciding the general worth of a financial backer’s holding. It’s urgent to screen the smallcase share price, as it shows the exhibition of the subject or procedure the financial backer has decided to put resources into. Understanding the variables impacting these costs is central to settling on informed speculation choices.
Factors impacting smallcase share prices include
- Execution of Part Stocks: The singular presentation of stocks or ETFs inside the Smallcase directly influences its general offer cost. Consequently, observing the basic protections’ presentation is basic in surveying the Smallcase’s development.
- Market Patterns and Monetary Circumstances: Outside economic situations, financial indicators, and worldwide events assume a critical role in impacting smallcase share prices. Understanding what these elements mean for the picked Smallcase topic or system is essential for anticipating potential cost developments.
- Rebalancing and Reconstitution: Some Smallcases go through intermittent rebalancing or reconstitution to keep up with the first venture proposal. Changes in the Smallcase piece can influence its portion cost, expecting financial backers to remain updated on such alterations.
High return Smallcase addresses the addition or loss on the speculation made in a specific Smallcase. It is a proportion of the portfolio’s exhibition over a particular period, frequently determined as a rate.
Central issues connected with Smallcase returns include
- Execution Appraisal: Smallcase returns permit financial backers to evaluate the outcome of their chosen speculation subject or procedure. It assists in understanding how well the portfolio has performed compared with the market or other venture choices.
- Risk Assessment: Breaking down returns supports assessing the gamble related to a Smallcase. More significant yields might demonstrate higher gamble, and understanding this equilibrium is vital for investors looking for an ideal risk to bring their profile back.
- Independent direction: Smallcase returns assist financial backers with settling on informed choices. By investigating verifiable returns, financial backers can check the possible future performance of a Smallcase and change their speculation methodology in like manner.
Conclusion
Smallcase share price and returns are critical markers in assessing the performance of a picked speculation portfolio. For those wandering into the universe of Smallcases, understanding the elements of offer costs and returns is critical. Watching out for market developments, individual stock execution, and monetary elements impacting Smallcases is basic for successful investing. At last, an educated dynamic given an exhaustive comprehension of smallcase share prices and returns is the foundation of an even speculation system.